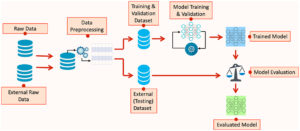
The rapid advancement of Artificial Intelligence (AI) is significantly reshaping how we approach epidemic forecasting and management. Predictive modeling, which involves using data and algorithms to forecast future events, has become an essential tool in understanding and controlling epidemics. AI enhances predictive modeling by analyzing vast amounts of data, identifying patterns, and making accurate forecasts that can inform public health strategies. This article delves into the role of AI in predictive modeling for epidemics, examining its applications, benefits, challenges, and future directions.
The Role of AI in Predictive Modeling for Epidemics
AI plays a transformative role in predictive modeling for epidemics by leveraging its capabilities in machine learning, data analytics, and pattern recognition. Traditional epidemic models often rely on historical data and simplified assumptions, which can limit their accuracy. AI, on the other hand, can process large and complex datasets, including real-time information, to provide more precise predictions.
Machine learning algorithms, a subset of AI, are particularly effective in predictive modeling for epidemics. These algorithms can analyze historical data on disease incidence, demographic factors, environmental conditions, and social behaviors to identify trends and make forecasts. For example, AI models can analyze data from previous outbreaks to predict how a new epidemic might spread, taking into account various factors such as population density, travel patterns, and healthcare infrastructure.
AI can also integrate diverse data sources, including social media posts, news reports, and search engine queries, to track public sentiment and detect early warning signs of outbreaks. This ability to harness and analyze non-traditional data sources enhances the accuracy and timeliness of predictive models, allowing for quicker responses to emerging threats.
Current Applications of AI in Predictive Modeling for Epidemics
AI’s applications in predictive modeling for epidemics are both diverse and impactful. One notable application is in the prediction of disease spread. During the COVID-19 pandemic, AI models were used extensively to forecast the trajectory of the virus, estimate the impact of various public health interventions, and guide policy decisions. These models incorporated data from numerous sources, including infection rates, mobility patterns, and vaccination coverage, to provide accurate forecasts and support decision-making.
Another significant application is in the identification of potential hotspots for future outbreaks. AI algorithms can analyze data on population movement, environmental conditions, and previous outbreaks to identify regions at high risk of new epidemics. For instance, AI models have been used to predict the emergence of zoonotic diseases—diseases that can be transmitted from animals to humans—by analyzing data on wildlife migration patterns and human-animal interactions.
AI is also enhancing the development of vaccines and treatments through predictive modeling. By analyzing genomic data from pathogens, AI can identify potential targets for vaccine development and predict how different strains of a virus might evolve. This information is crucial for developing effective vaccines and treatments that can keep pace with rapidly changing pathogens.
Benefits of AI in Predictive Modeling for Epidemics
The integration of AI into predictive modeling offers several significant benefits. One of the primary advantages is improved accuracy in forecasting epidemic dynamics. AI models can process large volumes of data, including complex interactions between various factors, to provide more precise predictions than traditional models. This enhanced accuracy enables public health authorities to make better-informed decisions and implement more effective interventions.
AI also contributes to faster response times. Traditional epidemic modeling often involves lengthy data collection and analysis processes. AI can analyze real-time data and provide immediate insights, allowing for quicker identification of potential outbreaks and more timely implementation of control measures. This rapid response capability is crucial in mitigating the impact of epidemics and preventing their spread.
Additionally, AI-driven predictive modeling can optimize resource allocation. By forecasting the progression of an epidemic and identifying high-risk areas, AI models help public health agencies allocate resources more effectively, such as deploying medical personnel, distributing vaccines, and setting up testing sites. This targeted approach ensures that resources are used where they are most needed, improving overall epidemic management.
Challenges in Implementing AI for Epidemic Predictive Modeling
Despite its advantages, implementing AI in epidemic predictive modeling presents several challenges. Data quality and availability are major concerns. AI models rely on high-quality, comprehensive data to make accurate predictions. Incomplete or biased data can lead to erroneous forecasts and ineffective interventions. Ensuring the availability of reliable data and addressing issues related to data privacy and security are crucial for the successful application of AI in epidemic modeling.
Another challenge is the complexity of epidemic dynamics. Epidemics are influenced by numerous factors, including human behavior, environmental conditions, and genetic variations. Modeling these complex interactions requires sophisticated algorithms and computational resources. Developing AI models that can accurately capture and predict these dynamics remains a significant technical challenge.
There is also the issue of model interpretability. AI algorithms, particularly deep learning models, can be complex and opaque, making it difficult for users to understand how predictions are generated. Ensuring that AI models are interpretable and transparent is important for gaining the trust of public health officials and ensuring that the predictions are used appropriately.
The Future of AI in Predictive Modeling for Epidemics
The future of AI in predictive modeling for epidemics holds great promise. Advances in AI technologies, such as enhanced machine learning algorithms and increased computational power, will continue to improve the accuracy and utility of predictive models. As more data becomes available and AI models become more sophisticated, we can expect even more precise forecasts and effective epidemic management strategies.
Integration with other emerging technologies, such as genomics and real-time monitoring systems, will further enhance the capabilities of AI in epidemic predictive modeling. For example, combining AI with genomic sequencing data can improve our ability to track and predict the evolution of pathogens, leading to more targeted and effective interventions.
Moreover, as global collaboration and data sharing improve, AI-driven predictive models will benefit from more diverse and comprehensive datasets. This increased data richness will enhance the accuracy of predictions and support more effective global responses to emerging epidemics.
Conclusion
AI is transforming predictive modeling for epidemics by providing advanced data analysis, accurate forecasts, and timely insights. Its applications in forecasting disease spread, identifying high-risk areas, and guiding vaccine development are revolutionizing epidemic management. While challenges such as data quality, model complexity, and interpretability need to be addressed, the future of AI in epidemic predictive modeling is bright. With continued advancements in technology and increased global collaboration, AI will play a crucial role in enhancing our ability to predict, prevent, and manage epidemics, ultimately leading to better public health outcomes worldwide.